Antibiotics play a crucial role in fighting bacterial infections, and one widely prescribed antibiotic is azithromycin. Azithromycin belongs to the macrolide class of antibiotics and is known for its effectiveness in treating a variety of infections. In this article, we will explore the uses, mechanism of action, potential side effects, and precautions associated with azithromycin. Understanding this antibiotic can help you make informed decisions about its usage and ensure optimal treatment outcomes.
Uses of Azithromycin :
Azithromycin is prescribed to treat various infections, including respiratory tract infections, such as bronchitis and pneumonia, as well as skin and soft tissue infections. It is also effective against certain sexually transmitted infections, such as chlamydia. Azithromycin works by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis, which helps in controlling and eliminating the infection. However, it is important to note that azithromycin is not effective against viral infections like the common cold or flu.
Mechanism of Action :
Azithromycin exerts its antibacterial effects by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit of bacteria, inhibiting the translation process. This action prevents the bacteria from producing essential proteins required for their survival and replication. By interfering with bacterial protein synthesis, azithromycin effectively halts the growth and spread of the infection, allowing the body’s immune system to eliminate the bacteria more effectively.
Potential Side Effects :
While generally well-tolerated, azithromycin may cause certain side effects in some individuals. Common side effects include gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. These effects are usually mild and resolve on their own. In rare cases, more serious side effects like allergic reactions, liver problems, and irregular heart rhythms may occur. It is important to promptly seek medical attention if you experience severe or persistent side effects.
Precautions and Interactions :
Before taking azithromycin, it is crucial to inform your healthcare provider about any existing medical conditions and medications you are taking. Certain medications, such as antacids, may interact with azithromycin and affect its absorption, so it is essential to follow the prescribed dosing instructions. Additionally, individuals with known allergies to macrolide antibiotics should exercise caution when using azithromycin. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their healthcare providers before starting this medication.
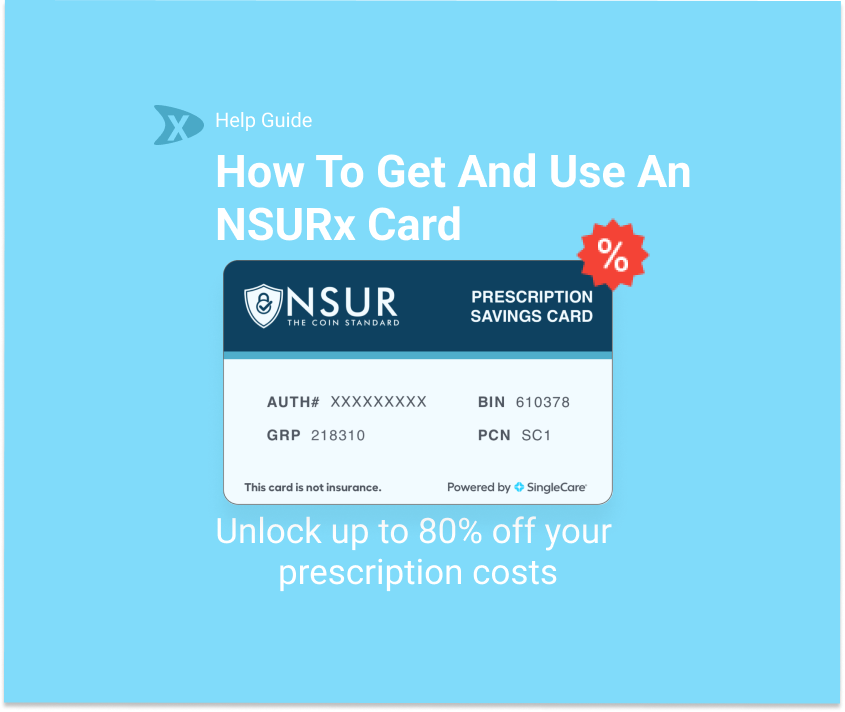
Take advantage of NSURx for your prescription drugs!
With the NSURx Prescription Benefit Card, you can save money on your medications at more than 35,000 pharmacies across the United States.
You can save up to 80% on your medication by using an NSURx card. Hundreds of dollars in savings could be yours every time you fill out your prescription.
The more you shop with NSURx, the more NSUR Coins you will receive as a reward.
Azithromycin is a valuable antibiotic widely used in the treatment of various bacterial infections. By understanding its uses, mechanism of action, potential side effects, and precautions, patients can make informed decisions about its usage and ensure optimal treatment outcomes. It is important to always follow the prescribed dosage and complete the full course of medication as directed by a healthcare professional. If you have any concerns or questions regarding azithromycin or its usage, consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
Disclaimer
This blog post is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider for personalized recommendations and guidance.